Table of Contents
How fast can Alligators swim?
Can Alligators Swim, Alligators can swim up to 20 miles per hour for short distances.
How long can alligators hold their breath underwater?
Like many reptiles, alligators can hold their breaths underwater for several hours. They shut down Blood flow to the lungs and other internal organs during normal activity.
Then when they need oxygen, blood is rerouted from the rest of the body to the lungs and they take a gulp of air. This is called a “gular pump.” It lets them swallow air even if their mouth is submerged underwater.
Do alligators like to swim? Do they like to be in the water?
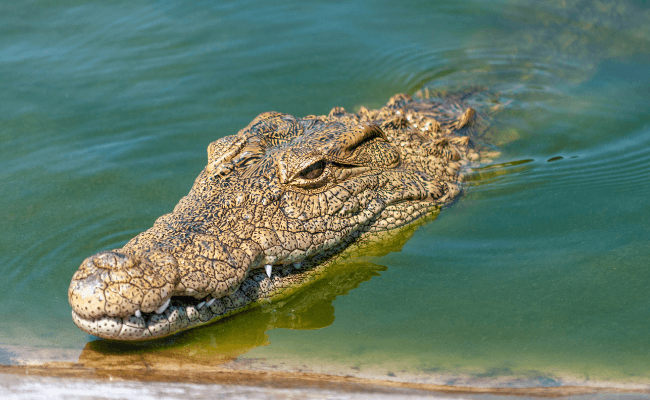
Alligators can and will swim anywhere: rivers, lakes, marshes, and swamps. They spend most of their time on land or in the water (about 80% of each). The only place you won’t find alligators is in the ocean.
How deep can an Alligators swim?
An alligator can stay submerged for several hours by inhaling air into their lungs. Underwater, an alligator’s heartbeat can drop to about 9 beats per minute, an adaptation that allows the reptile to go without breathing for extended periods of time.
The oxygen stored in an adult alligator’s body is sufficient enough to support resting metabolic rates for up to about 24 hours.
While submerged, an alligator’s eyes and nostrils are closed. The alligator swims by paddling with its powerful, splayed legs in a manner similar to a turtle’s four legs in a quadrupedal walk.

Adult American alligators can reach speeds of up to 3 miles per hour over short distances.
When confronted by an enemy, an alligator can swim vigorously in a rapid escape response or may attack suddenly with little provocation.
Such confrontations usually end quickly with the attacker retreating to avoid its prey’s deadly jaws and claws. When fleeing from danger, an adult alligator typically hides its head underwater, using only its eyes and nostrils for safety.
If an alligator is fully submerged, it usually cannot be seen because its dark gray color merges with the water.
Can Alligators swim in saltwater?
Many people have a question can Alligators swim in saltwater? An alligator can swim in saltwater. Some people think an alligator cannot live in saltwater but that is not true.
Alligators have a gland that removes excess sodium from their bloodstream, which means they don’t need to worry about the impact the high salt content has on other animals.
The gator could survive indefinitely if it had access to saltwater… but it still wouldn’t be a good idea. It can be done, but it’s better if they stick to freshwater.
Can Alligators bite underwater?
Yes, an alligator can bite underwater. Alligators are capable of holding their breath for up to an hour while swimming underwater in pursuit of prey.
How do Alligators catch their food?
Alligators use their strongest sense to find food: smell. A gator’s nostrils are located just over its eyes, so an alligator first finds its prey by sight and sound, then it submerges itself underwater to take a sniff. If the scent is right, the gator swims toward its prey and grabs it with its powerful jaws.
Do Alligators like to eat people?
Alligators generally don’t like to eat people. The truth is that most alligator attacks on humans are accidental.
An alligator is typically wandering around, minding its own business and hoping for a bite of fish or turtle… and then some careless person swims or wades into the alligator’s space.
Alligators are very territorial, and they see this as a threat to their home. The alligator will then proceed to bite the person or animal it thinks is intruding…
but in most cases, that person got too close for comfort, so the gator quickly let’s go when it realizes its mistake.
Is it dangerous to swim with Alligators?
Alligators are considered to be species that are normally not a threat to humans. They prefer a solitary life and avoid people at any cost.
However, alligators can be very dangerous if you get too close – even if they do not consider you as their prey. Since alligators have been on Earth for about 35 million years, they have learned how to survive and adapt to any environment.
They can even be found in the water surrounding Florida, where they use their aquatic skills as a means of protection against humans.
If you visit this state, it may be worth knowing more about how to stay safe around alligators before jumping into the water!
Can Alligators swim without a tail?
This is frequently asked question can alligators swim without a tail? In short, yes. Alligators can swim without a tail. However, they lose speed and maneuverability when swimming this way.
In addition to the loss of these qualities, an alligator’s tail also provides thrust when swimming. Without a tail, it would be difficult for an alligator to propel itself through the water.
An alligator’s front legs are long and powerful, but they have been modified into paddles that serve as extra pieces of oar-like equipment.
Although they can move on land without a problem with these limbs, their hind limbs are very short and help them keep a streamlined shape while swimming.

The alligator’s tail is flat and broad, with two lobes at the end that provides the alligator with a good source of propulsion in water.
The muscles along the tail are quite large and powerful, but their movements have been restricted by shortening tendons so they can only contract in a vertical direction.
This allows the alligator to raise its tail, but it cannot bring it down again without sinking.
A dead alligator’s tail is floppy and flaccid, with no muscle tone evident. It would simply drag behind the animal in the water until it decomposed if not for the tendons that keep it rigidly in place.
Can Alligators swim in cold water?
The short of this question can alligators swim in cold water is, “Yes.” While alligators are generally found in warmer climates where temperatures rarely if ever, drop below 60 °F (16 °C), they can tolerate somewhat cooler waters for limited periods of time.
Alligators are ectotherms whose body temperature is largely influenced by that their environment.
When water or air temperatures dip below 86 °F (30 °C), alligators slow their metabolic processes to a rate barely detectable by most of the hunting devices biologists use.
As a result, alligators have been known to survive in water as cold as 40 °F (4.4 °C) for several hours at a time. In fact, the American Alligator has occasionally been found in the wild in areas where it snows several times a year.






